The Evolution Of Cybersecurity In The Age Of Advanced Threats
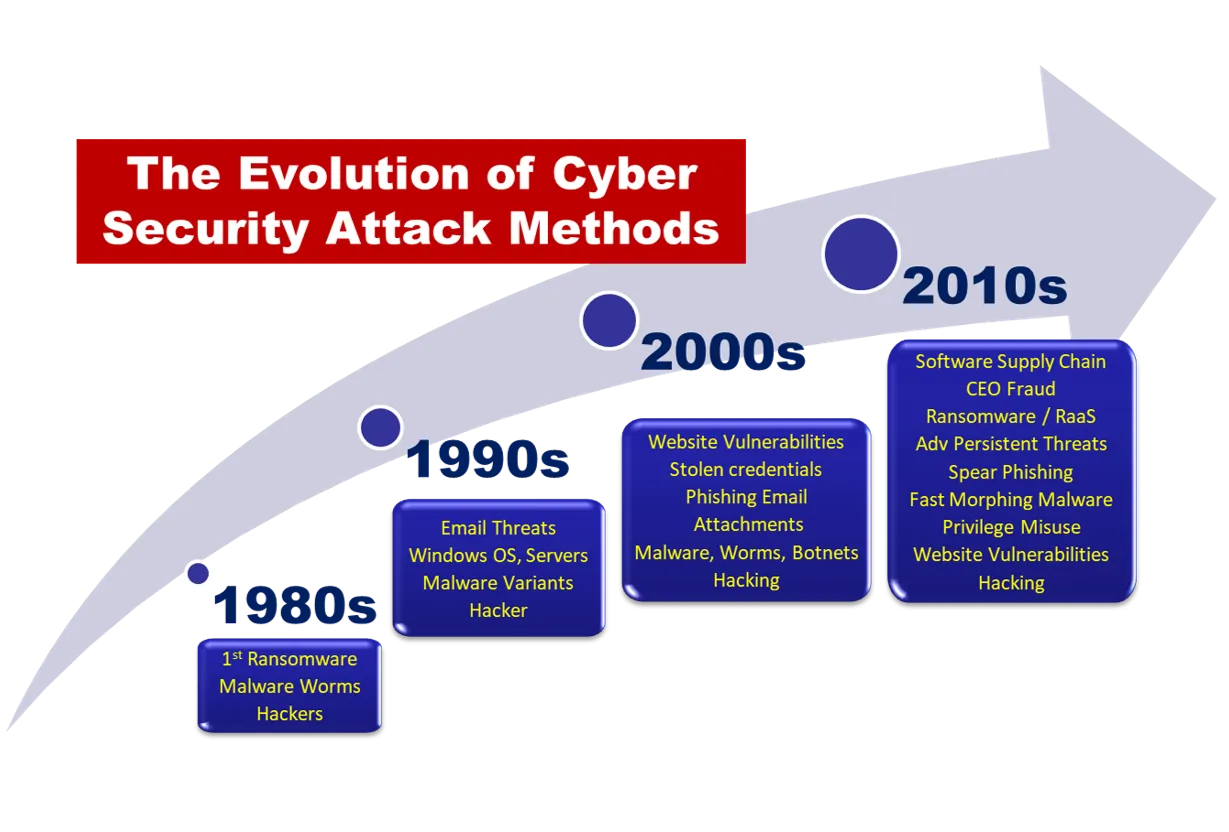
The digital landscape is evolving at breakneck speed, and with it, so too must the field of cybersecurity. Gone are the days of simple firewalls and antivirus software; today’s cybercriminals are armed with sophisticated tools and techniques, demanding a more nuanced and dynamic approach to defense.
In an era defined by unprecedented technological advancements, the evolution of cybersecurity has become a critical narrative. As organizations and individuals embrace the digital landscape, cyber threats have similarly evolved, becoming more sophisticated and potent. This article explores the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, tracing its evolution in response to advanced threats that permeate the digital realm.
1. The Advent of Cybersecurity:
– Early Years: Cybersecurity emerged with the proliferation of computers and the internet. Initially focused on building firewalls and antivirus programs to combat relatively simple threats like viruses and worms.
2. Rise of Malware and Exploits:
– Malware Proliferation: As connectivity increased, so did the prevalence of malware. From ransomware to spyware, attackers found new ways to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise systems.
– Social Engineering: Cyber attackers began employing social engineering tactics, manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information, circumventing traditional security measures.
3. Shift to Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs):
– Targeted Attacks: APTs marked a shift from indiscriminate attacks to highly targeted and sophisticated intrusions. State-sponsored actors and organized cybercrime groups sought specific information, often remaining undetected for extended periods.
4. Introduction of Machine Learning and AI:
– Adaptive Security Measures: The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence revolutionized cybersecurity. These technologies empower systems to adapt and learn from evolving threats, enhancing detection and response capabilities.
5. Securing the Cloud Environment:
– Cloud Adoption Challenges: With the widespread adoption of cloud computing, cybersecurity expanded its focus to secure data stored in cloud environments. Identity and access management became paramount in this decentralized landscape.
6. IoT Vulnerabilities:
– Expanding Attack Surface: The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices introduced new vulnerabilities. Cybersecurity efforts extended to safeguarding interconnected devices, preventing potential threats to smart homes, industries, and critical infrastructure.
7. Zero-Day Exploits and Vulnerability Management:
– Rapid Response: Zero-day exploits, targeting undiscovered vulnerabilities, became prevalent. Cybersecurity professionals adopted proactive vulnerability management strategies to identify and patch vulnerabilities swiftly.
8. Blockchain for Enhanced Security:
– Decentralized Security: Blockchain technology found applications in cybersecurity, offering decentralized and tamper-resistant ledgers. Its immutable nature enhances the integrity of critical data and transactions.
9. Ransomware and Extortion Tactics:
– Financial Motivations: Ransomware attacks surged, with cybercriminals encrypting data and demanding ransoms for decryption keys. Extortion tactics evolved, targeting businesses, healthcare, and even critical infrastructure.
10. Nation-State Cyber Warfare:
– Geopolitical Implications: Nation-states engaged in cyber warfare, utilizing advanced techniques for espionage, disruption, and influence. Cybersecurity efforts expanded to safeguard against geopolitical cyber threats.
11. Human-Centric Security Awareness:
– Human as the Weak Link: Recognizing the human element as a vulnerability, organizations prioritized cybersecurity awareness training. Employees became crucial in the collective defense against social engineering attacks.
12. Quantum Computing and Post-Quantum Cryptography:
– Future-Proofing Encryption: The advent of quantum computing posed a potential threat to existing cryptographic methods. Cybersecurity researchers explored post-quantum cryptography to ensure the resilience of encryption in the quantum era.
13. Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy:
– Legal Frameworks: Governments worldwide implemented stringent data protection regulations, such as GDPR. Cybersecurity evolved to ensure compliance and protect user privacy.
14. Threat Intelligence and Information Sharing:
– Collaborative Defense: The cybersecurity community embraced threat intelligence sharing to enhance collective defense. Information sharing platforms facilitated rapid responses to emerging threats.
15. Cybersecurity in the Age of AI and Automation:
– Autonomous Security Operations: AI and automation are increasingly utilized for autonomous threat detection, response, and mitigation. Cybersecurity operations evolve to keep pace with the speed and scale of modern threats.
The Future of Cybersecurity:
The future of cybersecurity will be defined by continuous adaptation and innovation. As threats become more sophisticated, so too must our defenses. Collaboration between governments, businesses, and individuals will be crucial in building a more secure digital world.
It’s a continuous battle, but by staying informed, adopting best practices, and supporting the ongoing development of cybersecurity solutions, we can navigate the ever-changing threat landscape and build a safer future for all.
Remember, cybersecurity is not just a technical challenge; it’s a human one. By understanding the motivations and methods of cybercriminals and prioritizing the security of our data and systems, we can ensure that the digital world remains a place of opportunity and connection, not fear and vulnerability.
Stay safe out there!
