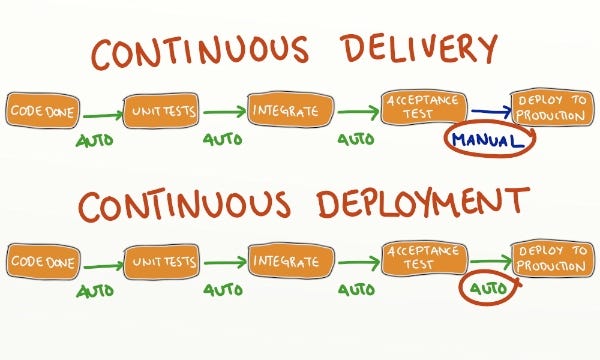
Continuous Integration And Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Best Practices
In the fast-paced realm of software development, the integration and deployment of code are critical phases that demand efficiency, reliability, and automation. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) practices have emerged as indispensable methodologies to streamline these processes, allowing teams to deliver software with speed, quality, and consistency. Let’s delve into best practices that can elevate your CI/CD pipelines to new heights.
Continuous Integration (CI) Best Practices:
1. Automated Builds:
Build Automation: Automate the process of building your application from source code to executable artifacts.
Consistent Environments: Ensure that builds are reproducible in consistent environments, minimizing discrepancies between development and production.
2. Version Control Integration:
Frequent Commits: Encourage frequent commits to the version control system to trigger CI builds regularly.
Branching Strategies: Implement effective branching strategies to manage parallel development efforts without compromising stability.
3. Automated Testing:
Comprehensive Test Suites: Develop and execute comprehensive test suites, including unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests.
Test Parallelization: Parallelize test execution to expedite feedback and identify issues early in the development cycle.
4. Code Quality Analysis:
Static Code Analysis: Integrate tools for static code analysis to identify code quality issues and enforce coding standards.
Code Coverage Metrics: Track and improve code coverage metrics to ensure thorough testing of code paths.
5. Artifact Management:
Repository for Artifacts: Utilize artifact repositories to store and version artifacts generated during the CI process.
Dependency Management: Manage dependencies efficiently, ensuring the availability of required libraries and packages.
Continuous Deployment (CD) Best Practices:
6. Automated Deployment:
Orchestration Tools: Leverage deployment orchestration tools to automate the deployment process across different environments.
Rollback Mechanisms: Implement automated rollback mechanisms to revert to a stable version in case of deployment failures.
7. Environment Parity:
Consistent Environments: Maintain consistency between development, testing, and production environments to minimize deployment-related issues.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Use IaC tools to define and provision infrastructure, ensuring uniformity across environments.
8. Incremental Deployments:
Canary Releases: Gradually roll out new features using canary releases to a subset of users before deploying to the entire user base.
Feature Toggles: Implement feature toggles to enable or disable specific features at runtime, providing flexibility in deployment.
9. Monitoring and Logging:
Real-time Monitoring: Integrate real-time monitoring tools to track application performance and detect anomalies.
Centralized Logging: Implement centralized logging to facilitate debugging and analysis during and after deployments.
10. Security Considerations:
Automated Security Scans: Integrate automated security scanning tools to identify vulnerabilities in the code and dependencies.
Immutable Infrastructure: Consider adopting immutable infrastructure principles to enhance security by replacing instances instead of modifying them.
General CI/CD Best Practices:
11. Collaborative Culture:
Cross-functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between development, operations, and testing teams to ensure a shared understanding of CI/CD processes.
Continuous Feedback: Encourage continuous feedback loops to address issues promptly and iteratively enhance CI/CD pipelines.
12. Documentation:
Pipeline Documentation: Maintain clear and up-to-date documentation for CI/CD pipelines, including configuration details and deployment procedures.
Onboarding Documentation: Provide comprehensive documentation for onboarding new team members, enabling them to understand and contribute to CI/CD processes.
Conclusion:
Effective CI/CD practices form the backbone of agile and DevOps methodologies, enabling teams to deliver software rapidly and reliably. By embracing automation, emphasizing code quality, and integrating security measures, organizations can cultivate a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Implementing these best practices ensures that your CI/CD pipelines become not just tools but strategic assets that propel your software development lifecycle toward efficiency and excellence.
