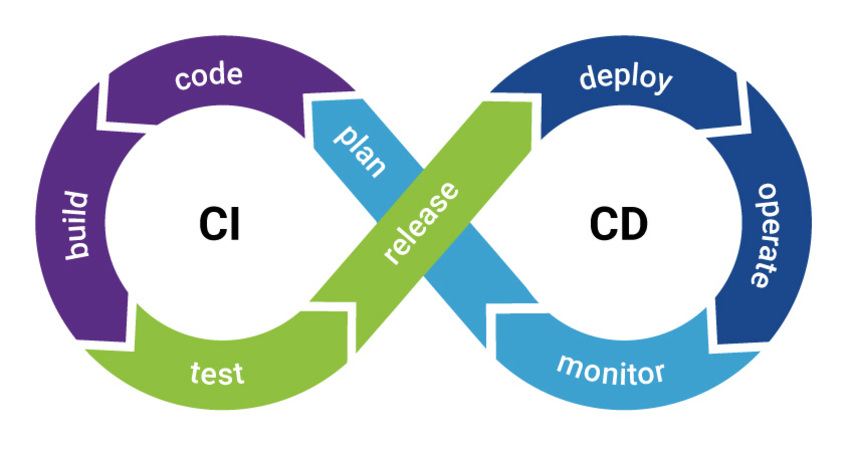
Continuous Integration And Continuous Deployment (Ci/Cd) Best Practices
In the dynamic realm of software development, where agility and speed are paramount, adopting Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) practices has become a necessity. CI/CD is a set of principles and practices aimed at automating the software delivery process, ensuring rapid, reliable, and consistent deployment. To harness the full potential of CI/CD, consider the following best practices:
1. Automate Everything:
– Description: Automate the entire build, test, and deployment process to eliminate manual interventions and accelerate the software delivery pipeline.
– Benefits: Reduces the likelihood of human errors, ensures consistency in the deployment process, and significantly speeds up the delivery cycle. This automation fosters a reliable and efficient workflow.
2. Version Control:
– Description: Use a robust version control system (e.g., Git) to manage and track changes in the source code, allowing collaboration and maintaining a history of alterations.
– Benefits: Enables seamless collaboration among developers, facilitates the identification of changes over time, and provides a safety net for rolling back to previous versions in case of issues.
3. Build Fast and Keep It Green:
– Description: Prioritize fast and reliable builds to obtain quick feedback on changes made to the codebase.
– Benefits: Accelerates feedback loops, allowing developers to identify and resolve issues early in the development process. Keeping the build “green” ensures a reliable foundation for subsequent stages of the pipeline.
4. Automated Testing:
– Description: Implement comprehensive automated testing practices, including unit, integration, and end-to-end tests, to validate the functionality and quality of the software.
– Benefits: Enhances overall code quality, catches and addresses bugs early in the development lifecycle, and instills confidence in the deployment process by ensuring that each code change passes a battery of tests.
5. Parallelize Builds and Tests:
– Description: Run multiple build and test processes concurrently to optimize resource utilization and speed up the overall build and testing phases.
– Benefits: Significantly reduces the time required for builds and tests, enabling faster feedback cycles and improving the overall efficiency of the development pipeline.
6. Artifact Management:
– Description: Employ artifact repositories to store and manage build artifacts systematically.
– Benefits: Ensures traceability of artifacts throughout the software delivery process, promotes reusability of components, and simplifies dependency management across different projects and teams.
7. Configuration Management:
– Description: Separate configuration from code and ensure it is easily configurable to accommodate varying deployment environments.
– Benefits: Enhances portability of the application, simplifies environment-specific configurations, and supports the deployment of the same codebase across multiple environments with minimal adjustments.
8. Continuous Deployment to Staging:
– Description: Aim for continuous deployment to a staging environment as a prelude to production deployment.
– Benefits: Identifies issues early in an environment closely resembling production, allowing for thorough testing before releasing changes to end-users. This practice mitigates risks associated with deploying untested code directly to production.
9. Immutable Infrastructure:
– Description: Treat infrastructure as code and employ immutable infrastructure patterns, where infrastructure components are replaced rather than modified.
– Benefits: Ensures consistency across deployment environments, simplifies rollbacks in case of issues, and enhances overall system reliability by reducing configuration drift.
10. Monitor and Analyze:
– Description: Implement robust monitoring and logging practices to track the performance and behavior of applications in real-time.
– Benefits: Enables the quick detection of issues, facilitates root cause analysis during incidents, and supports continuous improvement by providing valuable insights into system behavior.
11. Rollback Mechanism:
– Description: Establish a reliable rollback mechanism to revert to a stable state in case of deployment issues or unexpected behavior.
– Benefits: Minimizes downtime in the event of problems, providing a safety net for deploying changes with confidence, knowing that a rollback is available if needed.
12. Security as Code:
– Description: Embed security practices into the CI/CD pipeline to identify and address security vulnerabilities early in the development process.
– Benefits: Integrating security measures from the beginning helps in identifying and fixing vulnerabilities in a timely manner, reducing the risk of security breaches during production deployment.
13. Collaboration and Communication:
– Description: Foster collaboration and maintain clear communication among development, operations, and other stakeholders throughout the CI/CD process.
– Benefits: Enhances transparency, reduces silos between teams, and promotes a culture of shared responsibility, where everyone is aligned towards the common goal of delivering high-quality software.
14. Continuous Improvement:
– Description: Regularly review and enhance the CI/CD pipeline based on feedback, changing requirements, and emerging technologies.
– Benefits: Ensures adaptability to evolving needs, maximizes efficiency, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement where the CI/CD process is refined iteratively over time.
15. Documentation:
– Description: Maintain comprehensive documentation for the CI/CD pipeline, including processes, configurations, and best practices.
– Benefits: Facilitates onboarding of new team members, troubleshooting, and knowledge sharing, ensuring that the CI/CD pipeline remains transparent and accessible to all stakeholders.
By embracing these CI/CD best practices with a deep understanding of their descriptions and benefits, development teams can streamline their delivery pipelines, reduce time-to-market, and enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of the software development lifecycle. Continuous integration and continuous deployment not only accelerate software delivery but also contribute to a culture of collaboration, innovation, and continuous improvement.
